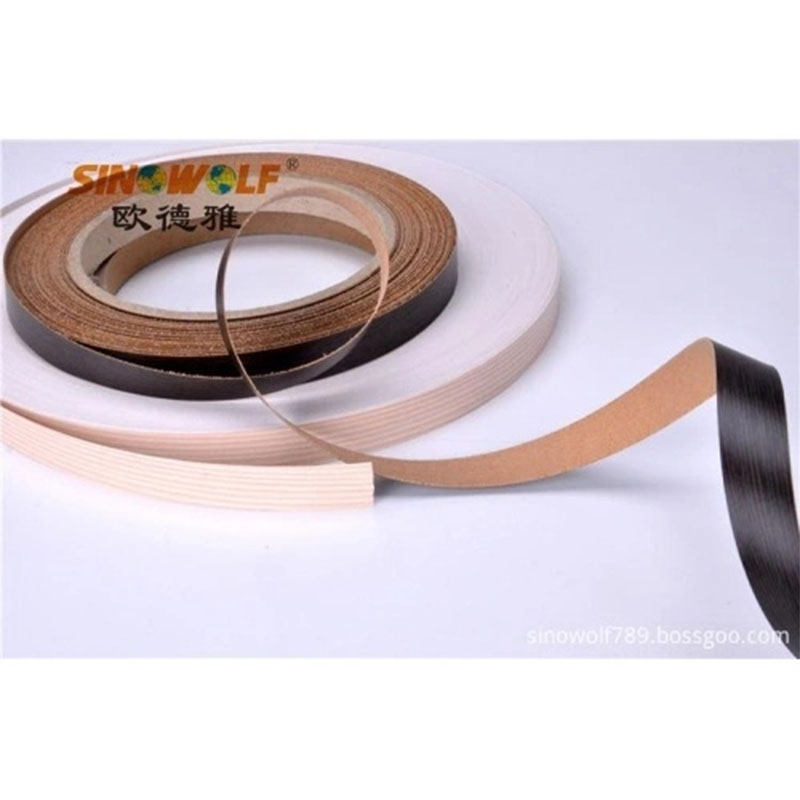
Edge banding is a critical process in cabinetry and furniture manufacturing, where the edges of panels are covered with a thin strip of material to improve appearance and durability. Hot melt adhesives (HMAs) play a pivotal role in this process, providing a strong, durable bond between the edge banding material and the substrate. Recent advancements in edge banding hot melt adhesives have introduced new formulations and benefits that are reshaping the industry. This article explores these advancements and their impact on the edge banding process.

1. Evolution of Hot Melt Adhesive Formulations
Traditionally, hot melt adhesives used for edge banding were based on EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate) or AP (amorphous polyolefin) resins. While these formulations have been effective, recent innovations have led to the development of new adhesive formulations that offer improved performance characteristics. Modern HMAs are now formulated with enhanced polymers and additives to address specific challenges in edge banding, such as bonding to diverse substrates and achieving superior durability.
One notable advancement is the introduction of reactive hot melt adhesives, which cure chemically after application. These adhesives provide a more robust bond and better resistance to environmental factors compared to traditional EVA and AP adhesives. Additionally, there are formulations specifically designed for high-temperature applications, which maintain their adhesive properties even in extreme conditions.
2. Benefits of New HMA Formulations
Enhanced Bond Strength: New formulations of hot melt adhesives have significantly improved bond strength, ensuring a more secure attachment of edge banding to the substrate. This enhancement reduces the likelihood of delamination and extends the lifespan of the finished product.
Improved Durability: Advances in HMA technology have led to adhesives that are more resistant to moisture, heat, and chemicals. This increased durability makes the edge banding more resilient in various environments, including high-humidity or high-temperature settings.
Versatility in Substrate Compatibility: Modern HMAs offer greater versatility in bonding to different substrates, including wood, MDF (medium-density fiberboard), and various plastics. This adaptability is crucial for manufacturers who work with a range of materials and need a consistent adhesive performance.
Faster Curing Times: New adhesive formulations feature faster curing times, which enhances production efficiency. Reduced setting times allow for quicker processing and shorter cycle times, leading to increased throughput in manufacturing.
3. Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is a growing concern in the manufacturing industry, and hot melt adhesive manufacturers are responding with eco-friendly formulations. Recent advancements include the development of low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) and solvent-free adhesives, which minimize the environmental impact of the edge banding process. Additionally, some new HMAs are based on renewable resources, further contributing to sustainable manufacturing practices.
4. Technological Integration
The integration of advanced hot melt adhesive formulations with edge banding machines has also seen significant progress. Modern edge banding machines are equipped with sophisticated control systems that optimize adhesive application. Features such as precise temperature control and automated adhesive feed systems ensure consistent application and enhance the overall efficiency of the edge banding process.
5. Case Studies and Industry Adoption
Several leading manufacturers have adopted new hot melt adhesive formulations to improve their edge banding processes. For example, a prominent cabinetry manufacturer reported a substantial reduction in edge banding defects and enhanced product durability after switching to a new reactive hot melt adhesive. These case studies highlight the tangible benefits of advanced HMA formulations in real-world applications.
6. Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the advancements, challenges remain in the adoption of new hot melt adhesives. Issues such as compatibility with existing equipment, cost implications, and the need for operator training must be addressed. Future developments in HMA technology are likely to focus on further improving performance, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing ease of use.
7. Conclusion
Advancements in edge banding hot melt adhesives represent a significant leap forward in the manufacturing of cabinetry and furniture. New formulations offer enhanced bond strength, improved durability, and greater substrate compatibility, contributing to higher quality and longer-lasting products. The incorporation of eco-friendly practices and technological innovations further supports sustainable manufacturing goals. As the industry continues to evolve, these advancements in hot melt adhesives will play a crucial role in driving efficiency and excellence in edge banding processes.